|
| Power Transmission Technology |
The demand for faster operation, higher quality output and increased efficiency has led to many of these improvements, and enhancements in motion control technology have brought some of the greatest gains. |

|
| One of these is the incorporation of anti-friction linear guides, commonly referred to as guide rails. These consist of contoured rails mounted directly to the machine axis, and recirculating ball or roller bearings, typically referred to as trucks or blocks. In order to appreciate the benefits of these products, let’s compare them to other available guidance systems. |
| A Tradition of Friction |
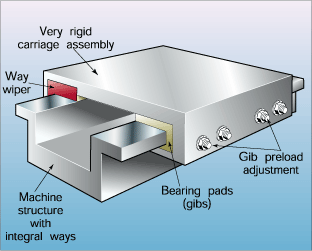
| Box ways are the grandfather of guidance systems. They consist of precision-ground surfaces, operating by sliding along the reference edges. Various configurations exist, but typically are either a “dove-tail” or “square-edge” design. In machine tools, box ways are used for directional control of the slide motion – keeping it “on track,” so to speak. The advantages of box ways are simple operation and design. The disadvantages are relatively high friction and relatively low speed capability. This has led designers to look for alternatives in order to increase speeds and reduce costs. |
|
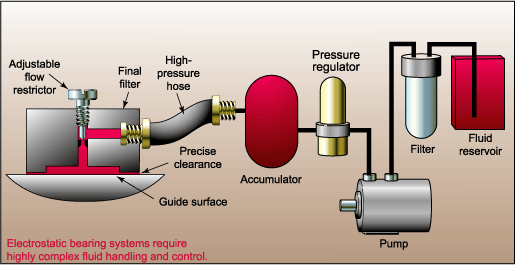
Box ways, left, offer simple operation and design, but at the cost of relatively high friction and low speed capability. On the other end of the spectrum, hydrostatic ways, below, offer very low friction and high speed capability, but at the cost of complexity and expense. |
|
On the opposite end of the guide spectrum are hydrostatic bearings. These employ a fluid film between the guide surfaces to reduce friction and vibrations. |
| The configuration requires a very elaborate, potentially expensive fluid handling system to maintain pressure and volume relationships. Hydrostatic bearings do, however, succeed in reducing friction and therefore increasing speed capabilities. |
| The Guide Rail Alternative |
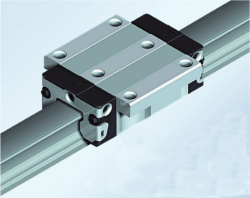
| In order to overcome these cost-versus-performance tradeoffs, many machine designers have come to rely on anti-friction guide rails as a best-of-both-worlds alternative. These systems, with their precision rails and low-friction, highly durable components, let designers achieve improvements in virtually all aspects of a machine’s performance: Speed, accuracy, ease of maintenance and repair, and manufacturing flexibility – all keys to a successful machine design. |

|
Due to demands of manufacturers worldwide, machine travel speeds are constantly increasing. Rapid feedrates in excess of 3,000 inches per minute are very common. High speeds such as this pose problems with friction and heat generation for sliding ways. High acceleration forces will increase the wear rate, as well. Linear guide rails can typically handle these speeds and accelerations with no detriment to performance.
Because the bearing elements roll instead of slide, the heat generated by a linear guide system is negligible. As a result, continuous rapid traverse is possible, and the wear associated with these adverse conditions is eliminated. |
|
| Additionally, the force required to move the slide is greatly reduced, which gives the machine designer more flexibility with motor and ballscrew selection. This flexibility in turn leads to cost savings. |
| What About Rigidity and Vibration? |
In some cases, the perception exists that linear guides are not as rigid as box ways, partly because, in the past, designers relied on massive structures to overcome the problems of unwanted vibrational forces. These designs also relied on massive bearing systems, which sacrificed speed and dynamic response, while at the same time increasing friction. In today’s high-performance machine tools, such compromises are unacceptable – speed, dynamic response and low friction are absolute requirements.
One solution is to adjust the spring characteristics of a linear guide type bearing system with preload to extend the natural frequency of vibration outside the normal operating range of the machine. This is all part of the modern approach to machine tool design, which views the bearing system as an integral part of the total design, yielding much higher speeds and dynamic response, while still addressing vibration concerns. |
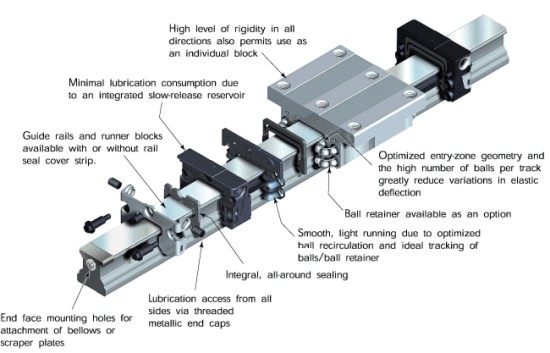
- Optimized recirculation results in 5 m/sec velocity and 500 m/sec2 acceleration
- Smooth and quiet running with optional ball retainer
- Minimal lubrication consumption due to integrated reservoir
- Mounting of attachments to runner block from above or below
|
|
|
Machine accuracy requirements are also becoming increasingly demanding, and the guide system plays a significant role here, too. Any deflection or clearance results in reduced accuracy. Sliding ways inherently have a small amount of clearance, which increases as the surfaces wear during operation. Again, guide rails can use preload to reduce clearances, or eliminate them altogether. Preload provides increased stiffness (rigidity), reducing the system deflection and improving machine tool accuracy.
The dimensional accuracy of the bearings themselves also reduces the tolerance stack-up. Most guide rail systems can achieve travel deviation tolerances in the 5- to 10-micron range (0.0002" – 0.0004") for the total length of stroke. Thus, the machine meets the performance criteria without incurring a cost premium. |
| Simplifying Maintenance and Repair |
| No machine design would be complete without consideration of maintenance and repair logistics. Sliding ways are often designed to become part of the structure of the axis. Some machine builders even cast the ways into the mold. In this case, field repairs are difficult, especially if components require removal and replacement. Guide rails, by comparison, are simply bolted to the casting, as are the blocks to the slide. This mounting arrangement often allows a technician to remove or repair the problem area without disturbing the complete machine. |

|
Whether the guides are provided in matched sets or, even better, as very accurate, individual, interchangeable components, the replacement costs and downtime can be drastically reduced. The machine builder can stock the product in service centers or at the factory, and have local technicians execute repairs on-site. |
|
| With box ways, the alternative is to return the machine to the factory or employ a machine repair shop – either of which can be costly to pursue. |
| More Flexibility for Machine Designers |
Lastly, the machine builders themselves benefit from choosing guide rails over sliding ways or hydrostatic bearings. Designers have the flexibility to use similar components on multiple machines. This reduces the manufacturing costs and inventory, and allows logistical flexibility in scheduling production. As mentioned above, repair stock can also be reduced. A wide array of sizes and styles are available to address any nuances of a particular design.
Designers can use the inherent accuracy of the guide system to reduce the requirements of positioning feedback and controls. Most designs now incorporate a rotary encoder in the drive motor for screw accuracy, and rely on the bearings to maintain lateral and height deviation within their dimensional tolerances. This is a very effective way to achieve performance without adding costly components. |
 |
Ongoing Innovation |
Guide rails themselves have seen important innovations recently. Many now feature clamping or braking components that grip the surfaces and secure a slide in place. Various sealing and lubrication enhancements are also available, both to protect the bearing environment and to reduce maintenance efforts and cost.
It is because of the demands outlined above, and the ability of guide rails to meet those demands, that linear guide systems are being selected at an ever-increasing rate. They allow smart machine designers to capitalize on their features and benefits, and pass those advantages along to machine tool customers in the form of improved performance, lower costs and innovative new features. |
 |
 |
|
 |